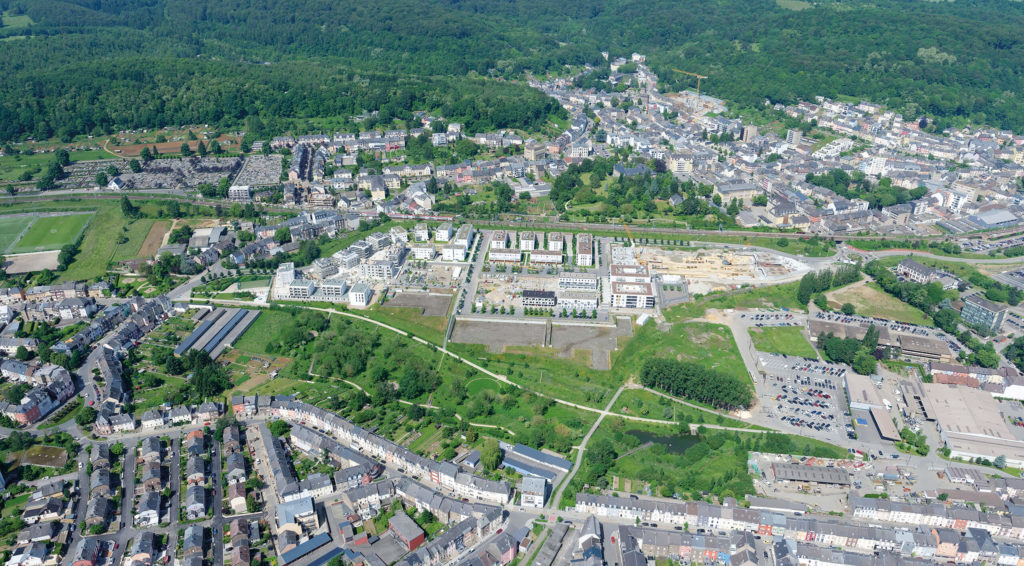
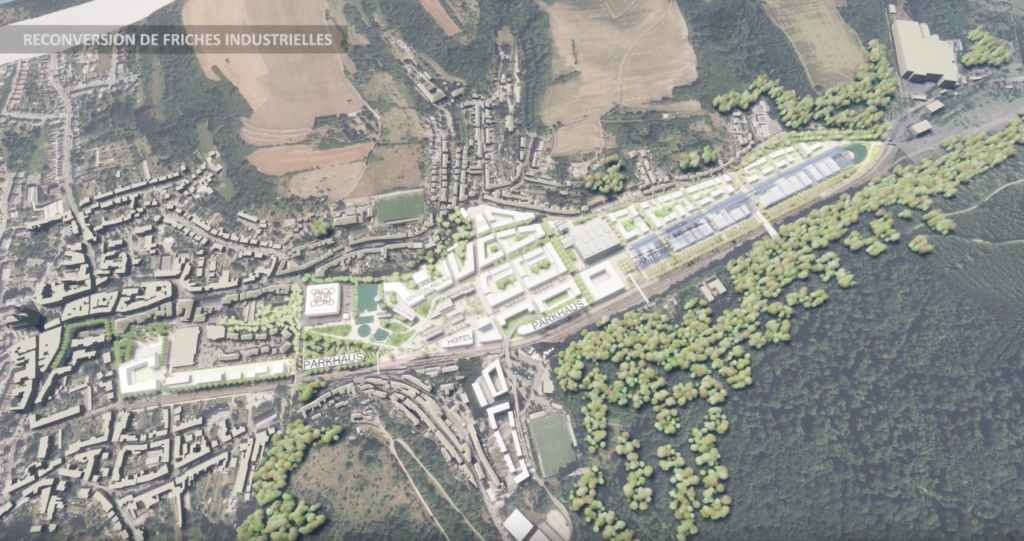
The Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, at the heart of Europe, continues to gain about 2% in population every year. The South of the country, the former industrial area, is growing especially rapidly, by a quarter since 2010 and in 2021 it hosted a third of all residents. Demand for housing has increased and is one of the most rapidly increasing expenses for Luxembourg households today.
In the already urbanised South, many large-scale development projects for new districts on industrial brownfields are being realised or are in the pipeline. This impacts the urban morphology of the area. Formerly geographically separated urban districts are now connected. But how can new districts interconnect urban fabrics, let alone urban functions? Differdange, the third largest city in Luxembourg, is home to such a brownfield project, ‘Plateau du Funiculaire’.
Rationale for action
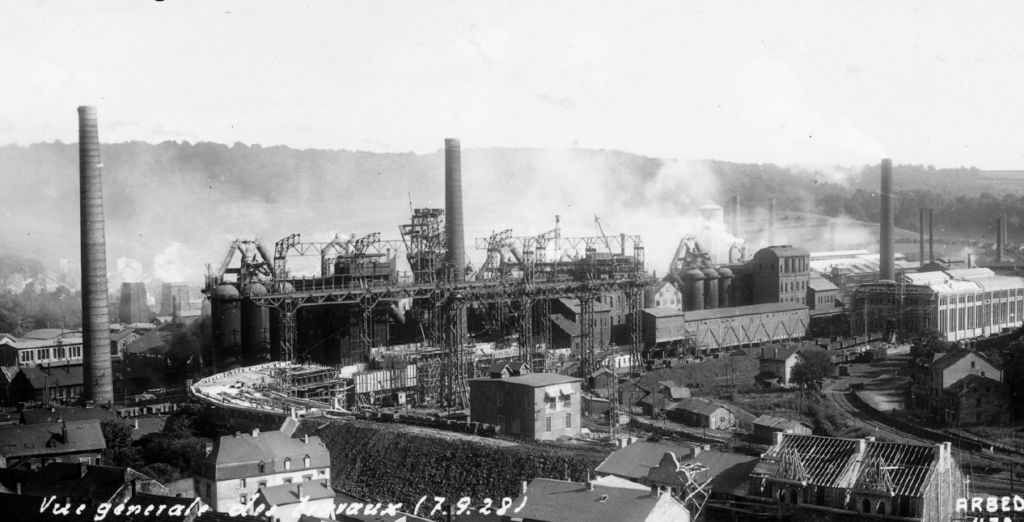
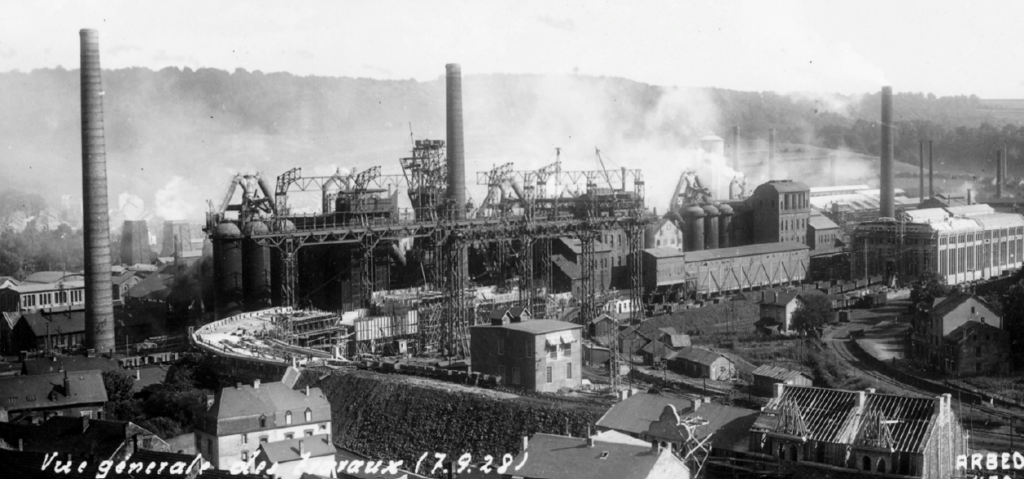
The rapid development of the steel industry in Luxembourg during the 19th and 20th centuries created a unique urban tissue in the South. Housing was built around steel mills, as in other industrial areas. This resulted in large industrial zones being next to urban centres. In some cases, as in Differdange, these industrial zones are ‘wedges’, impermeable barriers that separate districts functionally.
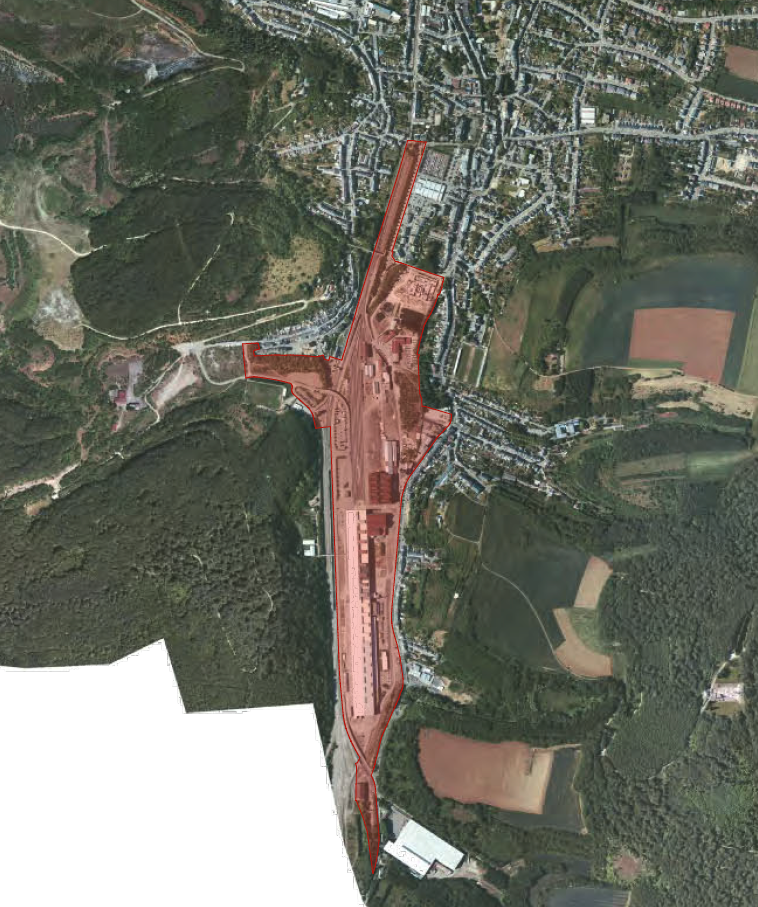
Steel production in Luxembourg has declined over several crises and steel mills have reduced or entirely stopped production. Around 2000, some 25 hectares became available in the centre of Differdange. The ‘Plateau du Funiculaire’ was formerly a landfill for the adjacent steel mill.
Objective
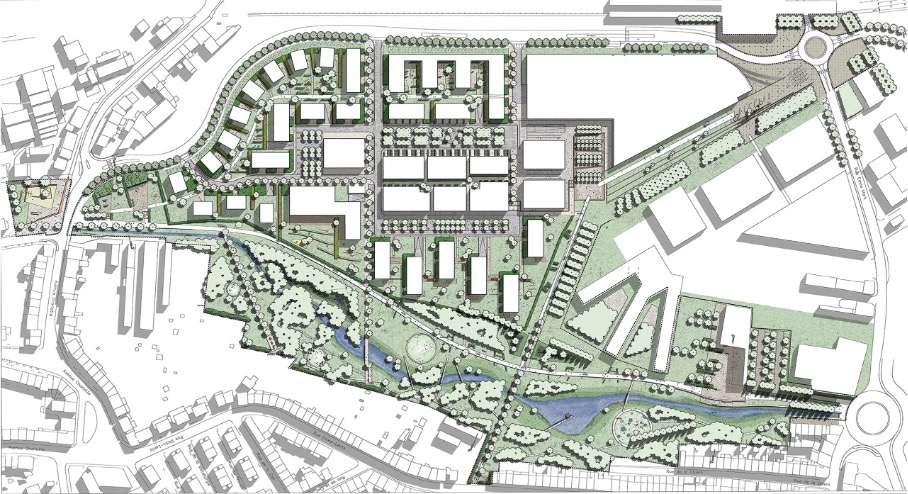
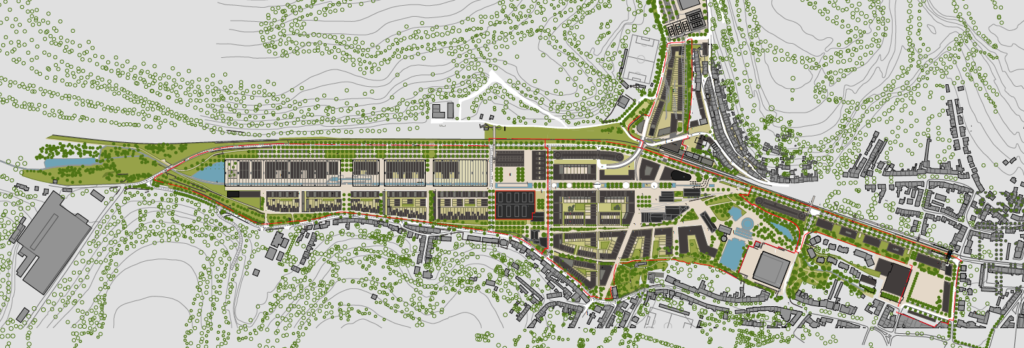
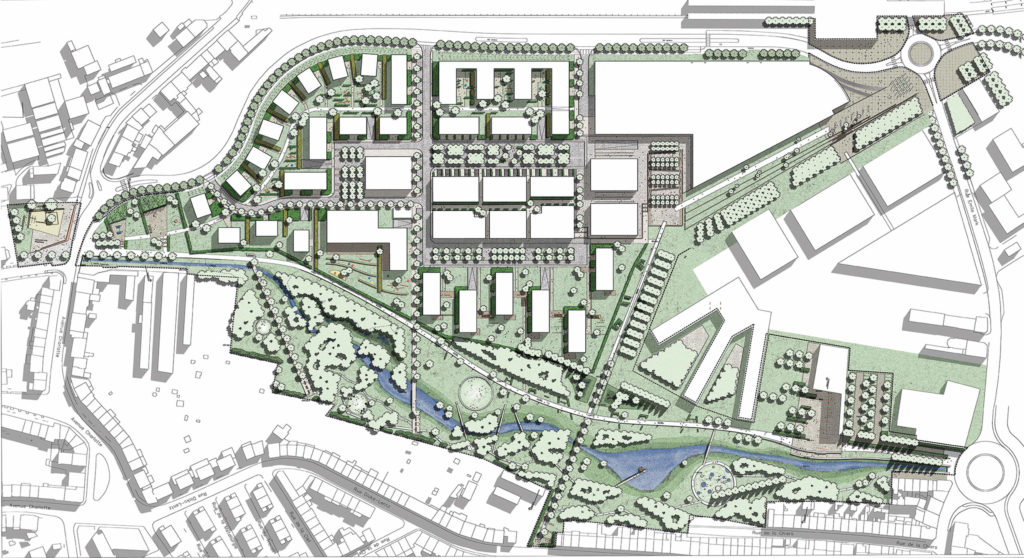
The Plateau du Funiculaire functionally split several Differdange districts, so plans were drawn up to transform the brownfield site into a new urban district. From 2004, the city has developed urban concepts in cooperation with many local and national players. A new district, providing housing, offices and commercial areas is planned to connect the existing districts of Differdange, Oberkorn and Fousbann.
Some challenges had to be addressed in developing the urban concepts, including pollution of the area due to its use as landfill for the blast furnace. In addition, the river Chiers running through the area was planned to be renaturalised, to provide water retention and flood areas.
Time frame
The first scoping studies were realised as early as 2004. Since then, planning and construction has been ongoing with most of the district being finalised in 2020. Final construction during 2022 will complete the project on the former landfill.
Key players
The key player for developing the new area was the city of Differdange. The urban concept was developed with a Luxembourg planning office as well as an investor.
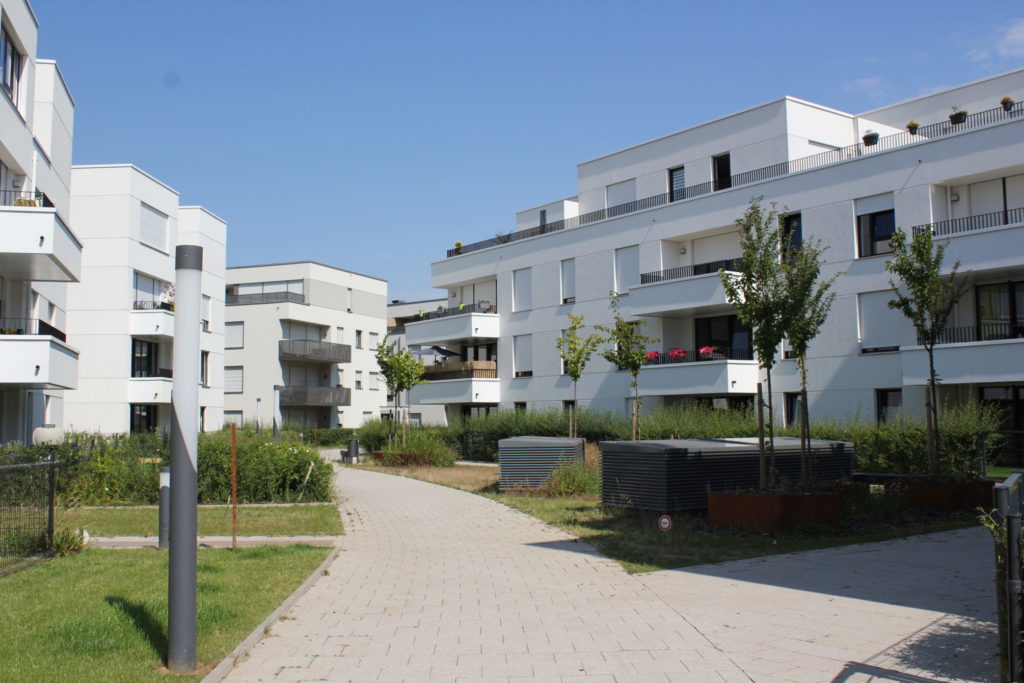

Implementation steps and processes
Following the first plans to develop the district in 2000, initial research in 2004 assessed the landfill pollution. At the same time, the city of Differdange also outlined strategic objectives for the district. In 2005, a planning office proposed the look and feel of the new district as an urban concept. Development started in 2006 when the historic ‘Villa Hadir’, a former reception and administrative building for the blast furnace was refurbished. Plans to implement the urban concept were submitted for building permits.
A brand was created in 2007 to establish an urban identity to market the new district to future inhabitants, businesses and commerce. Work on the infrastructure started in 2009 and the first bricks for the residential buildings were laid in 2011. In the same year, the recreational park was finalised, allowing neighbourhood residents to get to know the new urban district. Around 2019, a late change to the project integrated a multi-functional tower, called ‘Gravity’, increasing the number of planned housing units from 650 to 728.
Required resources
The resources used are not known.
Results
After a bit more than a decade of construction, the new district will be finalised in 2022. Within 10 years, 728 housing units have been created, providing accommodation for more than 1,600 people. The district also features 15 km2 of office and retail area. A school, a section of Luxembourg university, public administrative offices and shops complement the housing so the district is a fully developed urban quarter of Differdange.
A new train station links the area to the national railway network. In addition bus connections as well as bike and pedestrian infrastructure connect the district both internally and to the surrounding areas.
To minimise soil sealing, ‘Plateau du Funiculaire’ is high density. Nevertheless, some polluted parts of the former landfill were sealed with an artificial layer of clay so surface rainwater can drain into the nearby river. Rainwater that penetrates polluted soil layers is collected separately for treatment.
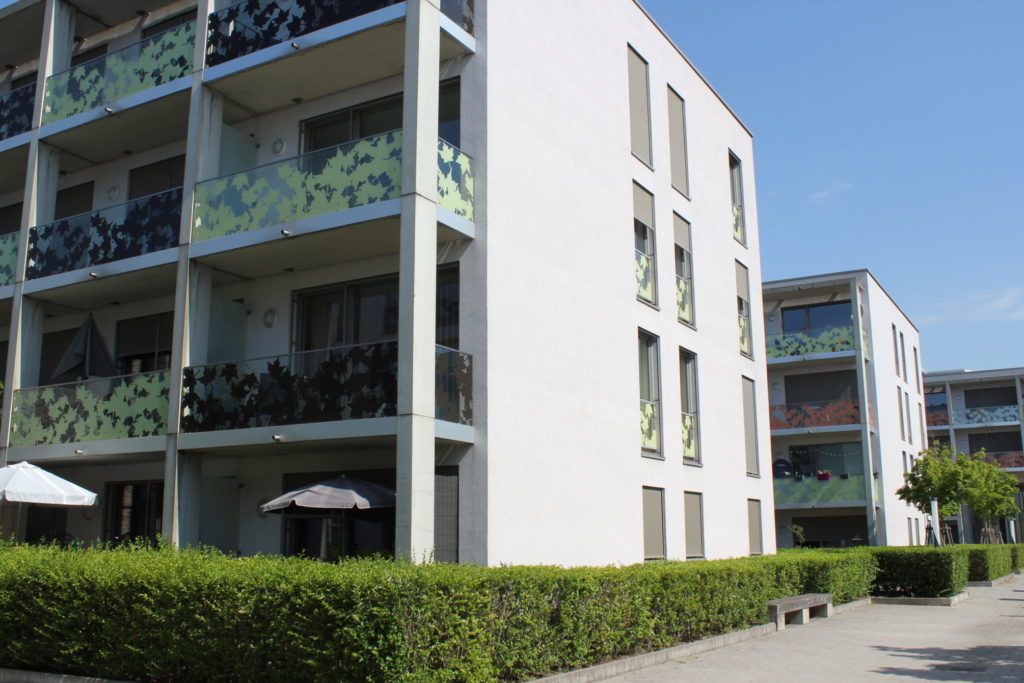

Experiences, success factors, risks
The relatively short construction period of ‘Plateau du Funiculaire’ highlights good preparation. Potential obstacles were identified, and solutions developed to avoid these.
The urban concepts and building permits provided planning security. The late modification to include a multi-functional tower in the district shows the project adapted to changing demands. Such flexibility is important as needs and requirements usually change for decade-long large-scale urban development projects.
Conclusions
‘Plateau du Funiculaire’ is a prime example of a successful large-scale brownfield development project. Such projects can close functional gaps between urban districts, offering new housing and commerce. In addition, interests from multiple public and private stakeholders can be addressed in one go. It also shows innovative approaches to issues like polluted soils that are frequently encountered in brownfield developments.
‘Plateau du Funiculaire’ also underlines that brownfield development offers much more freedom compared to developments in existing urban areas. Measures can be discussed before being realised in detail, helping to avoid conflicts.
In addition, brownfield development projects such as ‘Plateau du Funiculaire’ are testbeds for new approaches and technologies. The size of the district meant that planners faced challenges that could not be solved with existing planning approaches. An example is heating for the residential units where a centralised district heating system was planned as early as 2007 to reduce infrastructure costs and save energy.
Today the district offers a new face for Differdange and combines different urban functions in an optimal way. With multiple housing and commercial possibilities, ‘Plateau du Funiculaire’ will eventually become the new centre for the town.
Contacts
Urban technical service of Differdange: pag@differdange.lu
References
Dewey Muller, 2018: Plateau du Funiculaire project presentation (German): https://www.deweymuller.com/projekte/plateau-du-funiculaire/
Aurea Differdange, 2020: Project developer website (in French): https://www.aurea-differdange.lu/fr/localisation