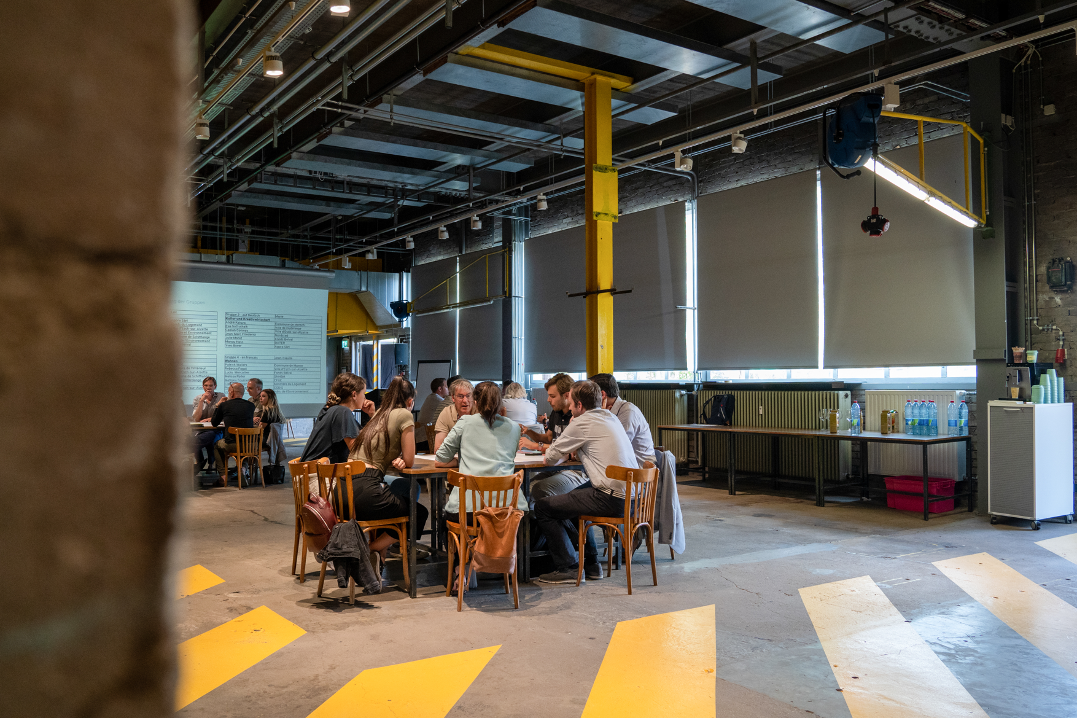
During the first workshop organised by the CIPU office in 2023 and held on the 27th of June, the participants delved into the concept of multifunctionality in the city, focusing on different scales (building/parcel, district, city). They had the opportunity to explore various planning examples and engage in discussions about the obstacles, potentials, and instruments associated with multifunctional urban use.

The day started off with an informative guided tour of the hosting location, the 1535° Creative Hub in the city of Differdange. The location symbolises creativity and innovation in Luxembourg. Established in 2013 by the city of Differdange, the Creative Hub got named after the melting temperature of iron at 1535°C, paying homage to the industrial heritage of the site and the whole city. Today it hosts creative and cultural start-ups, small- and medium-sized enterprises, artists, a co-working space as well as e.g. rentable music studios. More than just the physical space, the 1535° Creative Hub follows a community-driven approach, facilitating collaboration and sharing of expertise among its members. It functions as an open platform fostering synergies and networking, connecting actors from the cultural and creative industry and creating an open-minded environment for the sector.

After discovering the site, the workshop participants received input on functional mix in urban areas and its current relevance in Luxembourg. As a cross-cutting topic in the Master Programme for Spatial Planning 2023 (Programme Directeur de l’Amenagement du Territoire), it is primarily addressed under the objective of reducing soil artificialisation. In addition to that, the topic is considered under the objective of concentrating of different functions through e.g. creating Centres of development and attraction (Centres de développement et d’attraction). Furthermore, two examples developed during the Luxembourg in Transition Process (LiT) were presented, i. e. the densification strategy for the cross-border town Esch-sur-Alzette (LU) and Audun-le-Tiche (FR) as well as the plan for the commercial area Foetz to be transformed into a mixed-use zone. The local input was complemented with several examples from international multifunctional planning processes form Paris, Bern, Linz, Hamburg, Brussels and Anderlecht.

Finally, the participants delved into discussions on multifunctionality in urban spaces. The focus was on exploring the potential of integrating multiple functions within city structures on different scales (building/parcel, district, city). Through interactive sessions and planning examples, the workshop shed light on the obstacles, potentials, and instruments associated with multifunctional use in various contexts.
Working in groups, the participants explored multifunctionality in three key areas: commerce and services, production and manufacturing, and the creative sector and culture. These discussions considered the different existing scales, including the city, districts, and individual plots. The fourth group addressed the multifunctional use of housing in combination with schools, shopping centres, and industrial sites. These group sessions provided valuable insights into the challenges and opportunities associated with integrating different functions within urban structures. The results were then presented and discussed in plenum. The results of the discussions will be available on the CIPU Website soon.
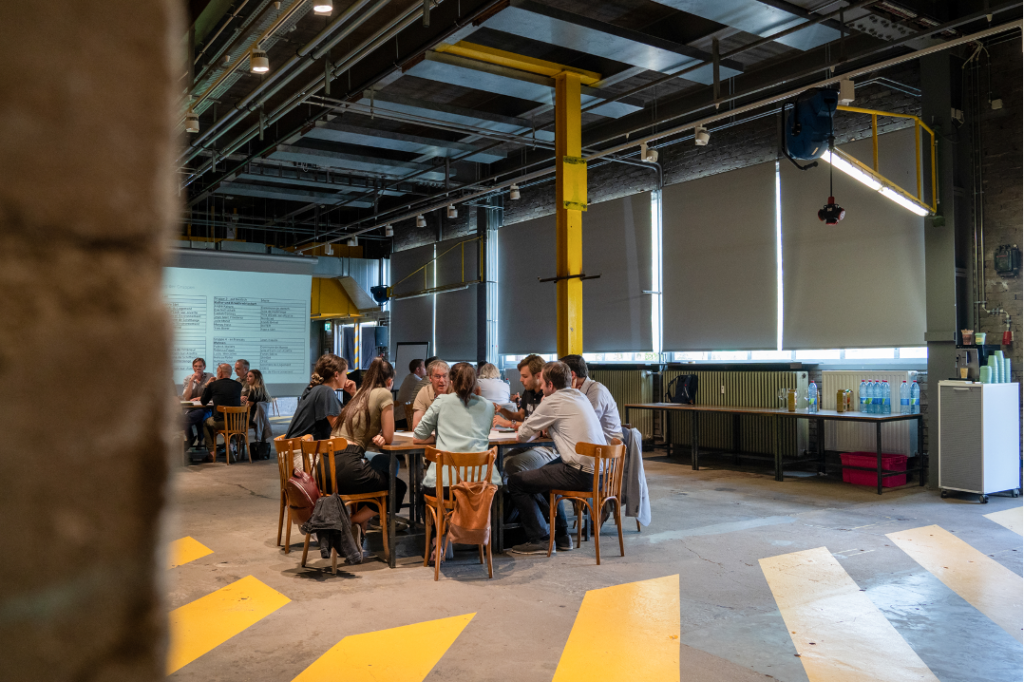

By examining multifunctionality at different scales, the workshop encouraged innovative approaches to urban planning and development. The participants considered the potential of multifunctional spaces to (re-)vitalise communities, optimise resource utilisation, and promote sustainable development. The workshop held within the CIPU framework offered a platform for collaboration and knowledge sharing, bringing together diverse perspectives from local and regional/national stakeholders as well as from thematic experts. It highlighted the importance of considering multifunctionality as a crucial aspect of contemporary city planning as well as which challenges need to be addressed by already existing and potential instruments.
Contact
- CIPU: cipu@zeyenbaumann.lu
References
- CIPU website (French and German): https://site.cipu.lu/
- PDAT 2023 (French): https://amenagement-territoire.public.lu/fr/strategies-territoriales/programme-directeur.html